PTW technologies evolution
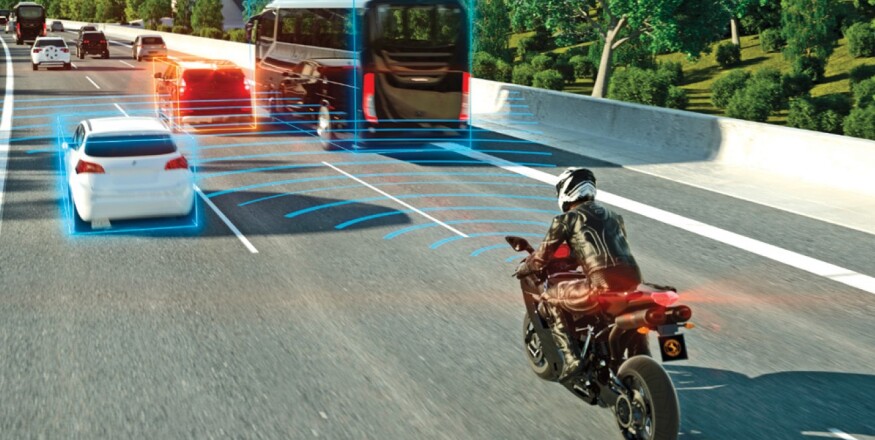
ACEM members continue supporting safety improvements, such as advanced motorcycle design, new intelligent features, new braking-, lighting-, suspension- and rider assistance systems. These technologies can help prevent accidents and contribute to collision reduction by supporting riders in critical situations. State-of-the-art technologies are deployed on different PTW segments considering their specific characteristics and use on the road.
Latest generation ARAS have moved from reactive systems to perceptive systems that are designed to monitor the motorcycle's surroundings in the front and in the back using radar sensors, to monitor the environment and detect potential hazards. These perceptive systems complement rider awareness and give the rider a warning.
Despite these evolutions in safe vehicle technologies, ACEM stresses the technological and user-based limitations of these technologies and therefore promotes the need for continued riders’ awareness and education for proper and optimised use of vehicles to maximise riding benefits on the roads.
To facilitate this, ACEM continues to be committed to a collaborative approach with all other road safety advocacy stakeholders to raise awareness of safe vehicle technologies (Euro NCAP, ETSC, ACEA).
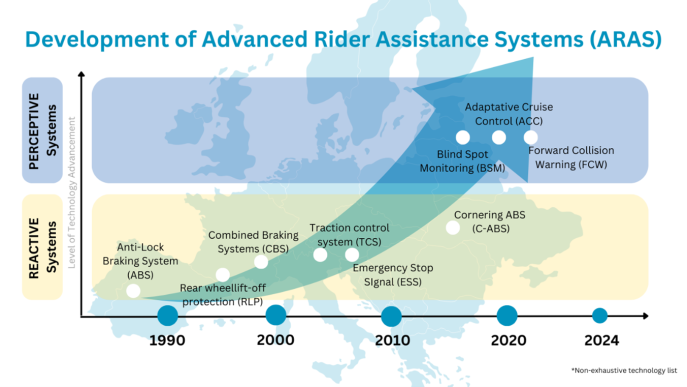
Non-exhaustive evolution of Advanced Rider Assistance Systems
STOPPING RIGHT IN TIME
Since 2004, ACEM members, as signatories of the European Road Safety Charter, have consistently demonstrated their commitment to motorcycle safety by equipping their models with advanced braking systems, such as ABS and CBS. The industry proactively adopted ABS on all L3-A2 and L3-A3 models well before the regulation made it mandatory for those categories. Today, ABS or CBS is mandatory for all L3-A1 vehicles, with ABS market penetration reaching 90%among ACEM OEM members. Furthermore, ACEM members have pioneered technologies like cornering ABS, rear-wheel lift-off protection, brake force distribution, and brake-by-wire, which enhance braking performance.
Seeing and being seen
Being detected by other road users is critical in motorcycle accident prevention. To make visual vehicle detection easier, ACEM members committed to equip all their vehicles with automatic headlamp on technology (AHO) as of 2003. Daytime running lights (DRL) and amber position lights (APL) are also used by the industry to make motorcycles more detectable for other road users.
Other relevant technologies available on the market include polyellipsoid headlamps, full LED lights (headlights, taillights and indicators), projector headlights, adaptive lights and cornering lights which automatically adjust headlights to curves, making night driving considerably safer.
Suspension and stability systems
High-performing suspension systems allow vehicles to adapt to different road surface conditions. They are also necessary for smooth handling and braking, and to keep riders isolated from road bumps. Over the years motorcycle manufacturers have developed a wide range of innovative vehicle suspension systems for different motorcycle usages.
They include electronic suspension systems, speed-sensitive electronic steering stabilisers, semi-active suspension systems (which adapt the response of the suspension to road conditions, vehicle speed and driving style) and self-regulating suspensions. All these systems allow maximum stability and increase users’ control of the vehicle.

Vehicle stability systems combine stability control, traction control, ABS and dynamic power steering to improve the safety of the rider.
Rider assistance systems for motorcycles
Rider assistance systems can help prevent accidents and contribute to collision reduction by supporting the riders in critical situations. They can also offer convenience and enhance the experience of riding by making life easier for riders. Relevant examples include: traction control systems (TCS), tyre pressure monitoring systems (TPMS), electronic adjustable suspension, electronic cruise control, gear shift assistant, fuel economy assistant, proximity activation systems (i.e. keyless riding systems), in-vehicle navigation systems with safety related traffic information, adjustable vehicle riding modes, blind spot monitoring, and automatic stability control.
“assistance systems can help prevent accidents and contribute to collision reduction by supporting riders in critical situations".It is important to understand that many advanced driver assistance systems were initially engineered for cars. However, they can be potentially dangerous if applied to motorcycles without a dedicated approach. This is why ACEM members work on specific engineering solutions for rider assistance technology.



